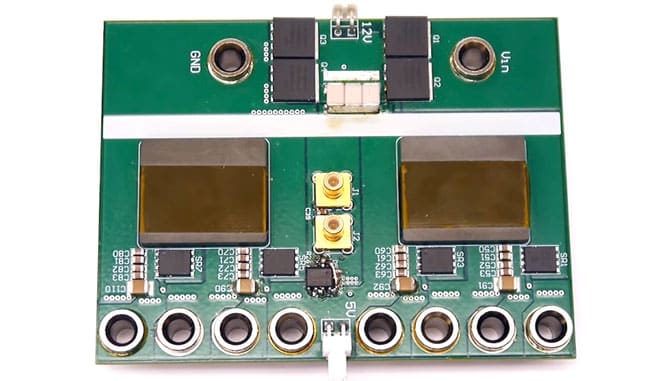
This article is based on newsletter blog written by Dr. Chema Molina, CEO of Frenetic that introduces pentacentra transformer topology for multiphase LLC converter in high-current data center applications.
The data centers consume more than 1,5% of the electric energy in the US, and researchers have been creating innovative solutions to improve efficiency.
The transformer topology most commonly used during the 2010s has been the LLC.
More than ten years ago, CPES published some articles and videos about this type of solution for LLC converters, where the idea was to integrate the transformer in the PCB, being very close to the switching devices, allowing very high switching frequencies up to 1MHz.
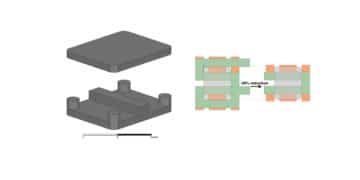
A new article by Chang Wang from the Technical University of Denmark and from the department led by Professor Andersen was published in TPEL about a new transformer configuration, the Pentacentra Transformer.
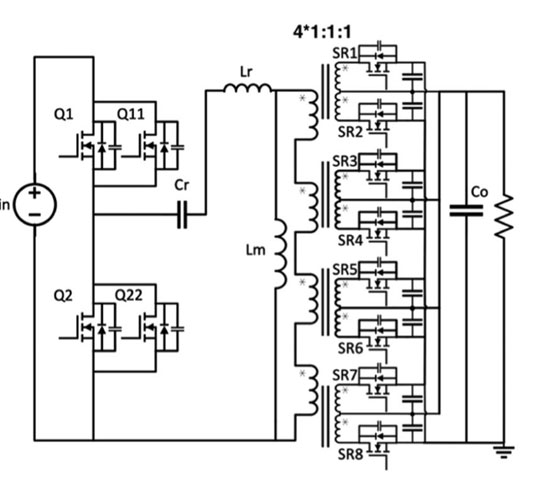
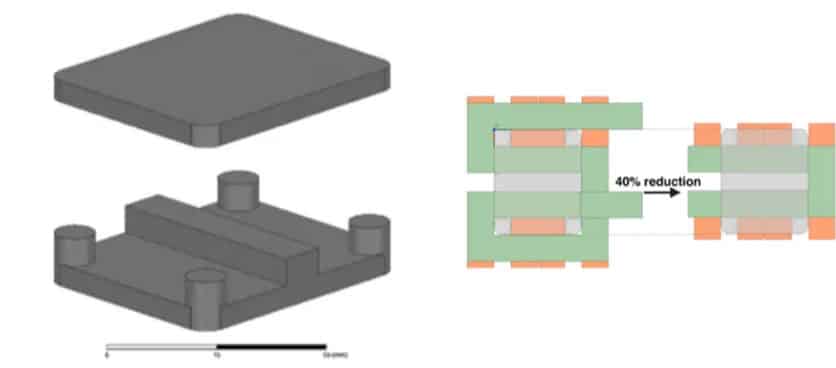
The main difference between the matrix and the Pentacentra is a central bar serving as the fifth leg of the core. The goal of adding this additional leg is to reduce by 40% the layout of the windings in the PCB. From my perspective, I would say it increases the complexity of the core, decreases the complexity of the PCB layout, and improves the overall efficiency.
The article explains with all detail the position of the rectifiers in the secondary, the current flowing paths.
They use the material ML91s from Hitachi. Very popular material in high-frequency publications.
GaN vs Si-FET
Another exciting thing that came out with the experimental results of the article is the comparison between the two prototypes. One uses GaN devices, and the second one uses Si. It’s the same board size.
The author explains that he needed to stop the test at 450 W in the GaN case because the device’s heat dissipation was worse than the Si-FET.
GaN devices are smaller than Si-FET, so, the heat dissipation capacity is smaller. Finally, he finished the tests with the Si-FET devices reaching 98% efficiency and 96% at full power. I would love to see if there was a way of improving the GaN heat dissipation without increasing the cost.
Abstract:
The role of data centers has become significant in the era of information technology, and their operation consumes a substantial amount of energy. Therefore, the point-of-load converter or voltage regulation module used in data centers must have high efficiency and power density to deliver a large current to specific servers. A common bus voltage 48 V at the rack stage needs to be stepped down to intermediate bus voltage, which is 6–5 V in this case. To achieve this, a new pentacentra transformer was developed for a four-phase LLC converter. A centra bar serving as the fifth leg of the core is added to the conventional four-leg matrix transformer. The interleaving and integration of windings in the proposed pentacentra transformer enabled balanced current sharing and reduced conduction loss by 45% compared to the traditional winding layout. The experimental prototype of the converter was designed to achieve 800 W power output at a switching frequency of 500 kHz and 48 V–40 V/6 V–5 V voltage conversion. The peak efficiency achieves 98.1% along with the power density of 240 W/in 3 with the experimental result. Without the heatsink, the whole converter is operating at rated power within a safe temperature lower than 86°. The excellent thermal performance ensures the reliable operation of the converter and promises a larger power delivery capability.
Reference
[1] “Pentacentra Transformer for Multiphase LLC Converter in High-Current Data Center Application” Chang Wang , Student Member, IEEE, Mingxiao Li , Member, IEEE, Ziwei Ouyang , Senior Member, IEEE, Tiberiu-Gabriel Zsurzsan , Member, IEEE, and Michael A.E. Andersen , Member, IEEE
Read the original post at Pentacentra Transformer Benefits in High-Current Data Center Application