LAN and LAN RJ45 series Ethernet transformers
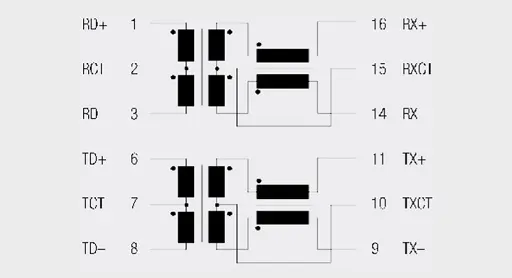
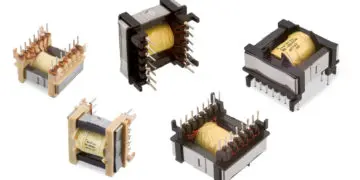
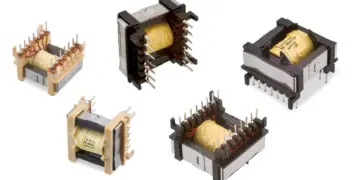
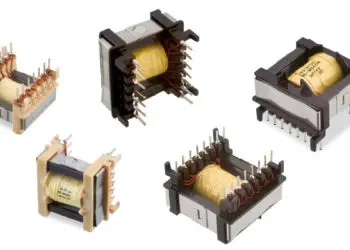
The LAN Ethernet transformers (Figure 2.82) are not simple transformers, but rather modules in which, depending on the number of ports for which they are suitable, at least two transformers and a certain number of current-compensated chokes are contained.

As the name denotes, they are designed as transformers for Ethernet networks. Ethernet is the most widespread form of local network (Local Area Network – LAN). Ethernet is operated at different transmission speeds. The requirements for Ethernet are described in the IEEE802.3 standards:
• 10 Base-T: transmission rate 10 Mbps > standard IEEE802.3
• 100 Base-T: transmission rate 100 Mbps > standard IEEE802.3u
• 1000 Base-T: transmission rate 1000 Mbps > standard IEEE802.3ab
• Power over Ethernet: independent of the transmission rate > IEEE802.3af
For these standards, the transmission medium is a copper cable with unshielded, twisted pairs (UTP) of type CAT5 or better. The other IEEE802.3 series standards refer to glass fibre cable transmission.
For 10 Base-T and 100 Base-T, one wire pair is used for the transmission channel (transmit) and one for the reception channel (receive). Two of the four wire pairs in the Cat5 cable remain unused. In the case of 1000 Base-T, all four wire pairs are used in both directions.
According to the EN60950 standard (safety of information technology equipment), Ethernet is classified as a TNV 1 circuit (telecommunication network voltage). It has to be isolated against a SELV circuit (safe extra low voltage). The test voltage stipulated by the standard must be at least 1.5 kV with a test duration of 1 min.
As a result of this isolation voltage, it is essential to use a transformer between the network and the Ethernet terminal device. So two transformers are required for 10/100 Base-T networks and four transformers for 1000 Base-T networks. The necessary number of transformers is integrated in the WE-LAN series modules. As described in the previous section, ring core transformers are used.
To avoid further external components, e.g. current-compensated chokes (data line filters), these are also integrated in the transformer modules (see Figure 2.83).
The relevant Ethernet standards for 100 Base-T call for transformers with a minimum inductance of 350 µH and DC current pre-magnetisation of 8 mA. This should serve to ensure functionality even with small asymmetries of the wire pairs.
The turns ratio is defined by the Ethernet controller used. Whereas 10 Base-T often uses turns ratios of 1 : 1.414 or 1 : 2.5 on at least one of the lines, 100 and 1000 Base-T almost exclusively work with a turns ratio of 1 : 1. This is because the number of secondary turns is so large – due to the high primary inductance combined with a higher number of turns than with 10 Base-T – that they can no longer be accommodat ed on a small ring core. Winding with twisted wires is also no longer possible, which can still be tolerated for 10 Base-T, but leads to a de terioration in transmission properties for 100 Base-T.
The minimum insertion loss and the maximum values for return loss, crosstalk and common mode rejection are also defined over the entire frequency range.
ABC of CLR: Chapter L Inductors
LAN transformers
EPCI licensed content by: Würth Elektronik eiSos, Trilogy of Magnetics, handbook printouts can be ordered here.

This page content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License.
see the previous page: Applications for transformers
< Page 17 >
see the next page: Telecom transformers



















Discussion about this post