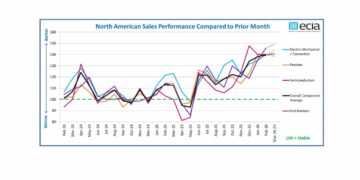
Murata Announces Building of Moriyama Innovation Center as a New Research and Development Hub
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (“Murata”), announces that it will establish the Moriyama Innovation Center as a new research and development (R&D) hub located in front of Moriyama Station in Shiga Prefecture. Construction begins in February 2024 and is...