Würth Elektronik’s Application Note ANP125 publishes the results of a study “The acoustic effects of harmonic distortion of aluminum electrolytic capacitors” on harmonic distortion of electrolytic capacitors. The result: Capacitors don’t cause any appreciable signal distortion.
The discussion is ongoing in the audio technology world about what circuit elements affect the sound quality of amplifiers.
The app note by Würth Elektronik provides empirical evidence to add to this discussion and answers questions that most audio engineers have.
Application Note ANP125 is the result of international research collaboration between R&D teams at production sites in Asia and the Würth Elektronik Competence Center in Berlin. The text begins with an introduction to human hearing and psychoacoustics and goes on to examine harmonic distortions in capacitors. Furthermore, results from model calculations are presented in order to check the plausibility of the measured results. The measurements show no appreciable distortion of signals caused by capacitors.
Material variations also tested
Dr. René Kalbitz, Product Manager in the Capacitors & Resistors Division at Würth Elektronik eiSos and author of the study, explains:
“The investigations indicate that material variations have a negligible influence on distortions, and these are below the hearing threshold. Electrolytic capacitors do not add any appreciable harmonics to the fundamental frequencies in signal transmission, so, to a good approximation, they can be considered as linear components. It is likely that other voltage-independent capacitor types and passive components, as a rule, generate similarly low distortion amplitudes compared to the audibility threshold. Consequently, the choice of non-linear components such as operational amplifiers and diodes has a greater distortion impact on the audio quality of the amplifier, i.e., the overall distortion characteristics, than the choice of electrolytic capacitor.”
Abstract
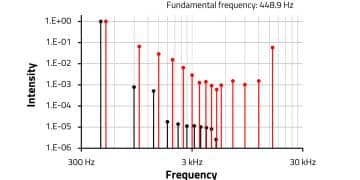
This application reports a study of total harmonic distortions (THD) caused by commercial electrolytic capacitors, as produced by Würth Elektronik eiSos, as well as purpose-built items.
In order to find parameters that influence the THD, capacitors with different separation paper and electrolyte compositions have been investigated. Those sample capacitors were assembled at near mass production conditions at a production site and analyzed at the electrical laboratory of Würth Elektronik in Berlin.
At first, the appnote provides an introduction into the field of human hearing and psychoacoustics before approaching the study of harmonic distortions in capacitors. It furthermore introduces results from model calculations to check the plausibility of the measured results.
The results suggest that the harmonic distortions are well below the threshold of audibility. It can be concluded that the capacitors do not add significant distortions to fundamental frequencies as they transfer signals. Modifications of the electrolyte or separation paper have a negligible effect on the THD.
Content:
- Introduction to human hearing
- THD of a Capacitor Model
- Experiment Details
- Measured THD of 470 µF Electrolytic Capacitor
- Comparative Analysis of Capacitors
See the detailed application report at the link here:
Read the original post at Acoustic Effect of Harmonic Distortions Caused by Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: Myth Denial