Source:source: Exxelia – Capacitors GBU,France; ESA SPCD 2018 Symposium
EPCI e-symposium library article
Miniaturization is a driving need for space applications. This need gives rise to the Surface Mounting Devices trend which allows to manufacture more and more compact equipment which at last are cheaper to produce and put on orbit.
But this evolution, which is true whatever the application is, implies some modifications in the manufacturing process of the ceramic chips capacitors and in the based material used to manufacture them. Two options have been considered by Exxelia to enable multilayer ceramic capacitors to withstand these new constraints:
- To design smaller capacitors (down to size 0402) and lowest rated capacitors (down to 10V), what means a complete work on the design rules and the manufacturing process of these products. The main challenge consists in reducing the dielectric thickness considered to manufacture the parts and to guarantee in the same way a sufficient reliability of these thin layers.
- To design alternative components with reduced losses in order to minimize heating. As losses are mainly due to the ceramic dissipation factor, such a choice implies a complete change of the ceramic dielectric. This second possibility lead up Exxelia Technologies to evaluate a new ceramic capacitors range based on a new dielectric material called C48X.
published by EPCI under approval of ESA SPCD 2018 organizing committee.
Title: Extension of the space qualified MLCC’s ranges
Author(s): Dr. Henri Laville(1), Maud Fabre(1)
Organisation(s): (1)Exxelia – Capacitors GBU, Z.A.E. du Clos du Chêne – 1, rue des temps modernes, F-77600 CHANTELOUP en Brie – France
Symposium: ESA SPCD 2018
Reference: Evaluation and Qualification 3.
ISBN: N/A
e-Sessions Applications: Aerospace
e-Sessions Scope Components: Capacitors
e-Sessions Topics: Technology, Specification & Qualification
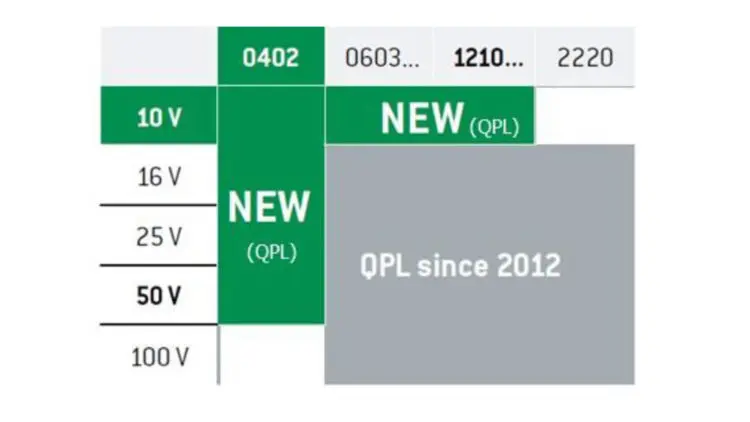
QUALIFICATION OF THE SIZE 0402 AND OF THE 10V RANGE
Technical Constraints
As a reminder, Exxelia already introduced in the QPL a full range of ceramic chips capacitors, from sizes 0603 to 2220, from 16V to 100V.
Exxelia went further and decided to qualify the size 0402 and the 10V range.
The qualification of these two new ranges has implied :
- To work on the design rules of the capacitors and in particular on the reduction of the dielectric thickness.
- To work on the manufacturing process in order to guarantee the reliability of these thin ceramic layers.
- To develop new equipments for the metallization (Figure 1) and the control of these very small capacitors.
Accessible ranges
Different configurations of terminations have been considered for this qualification:
- Ag/Pd/Pt termination
- Nickel barrier + Sn/Pb 60/40
- Nickel barrier + Gold
- Polymer + nickel barrier + Sn/Pb 60/40 or Gold : This polymer termination includes a soft layer which acts as a “stresses buffer” and prevent the chips cracking.
Qualification program
The qualification tests have been performed with the help of the French space agency (CNES) and are described in the generic specification ESCC n°3009 (Figure 2).
The qualified ranges are detailed in the Figure 3.
Figure 3 : New qualified ranges
EVALUATION OF THE NEW C48X CERAMIC
Technical Constraints
Two classes of dielectric are mainly used to manufacture ceramic capacitors. The first class is mainly composed of NPO ceramics. These ceramics are mainly made of titanium dioxide with a low dielectric constant (εr ≤ 100). These ceramics are very stable with only minor changes under stresses of temperature, voltage and frequency.
The second class is composed of X7R ceramics. These ceramics are mainly made of barium titanate with perovskite structure and have a high dielectric constant (1000 ≤ εr ≤ 5000). The counterpart is that these ceramics present some noticeable variations under temperature, voltage and frequency
With the aim of changing the dielectric material used to manufacture Exxelia high voltage ceramic capacitors, what was Exxelia’s first goal, it was obviously necessary to use a ceramic whose performances would allow to:
- Develop ranges with the same capacitance / voltage / volume characteristics than the X7R dielectrics
- Dissipate less energy than X7R materials, what means selecting a dielectric with a dissipation factor much lower than X7R’s dissipation factor –which is typically for high voltage parts equal or greater than 50.10-4.
Our choice has been a dielectric with an intermediate dielectric constant value (about 450). This material can be processed using a greater voltage gradient (ratio of voltage and dielectric thickness) than X7R dielectrics so that its capacitance per volume could be comparable with the capacitance per volume of an X7R material.
Dielectric Performances
The main characteristics of the selected material which combines most of the advantages of NPO and X7R materials are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 : Main characteristics of “C48X” material
|
Dissipation factor at 1kHz, 1Veff : |
≤ 10.10-4 |
|
Typical DF at 400Hz, 1Veff : |
≤ 5.10-4 |
|
Insulation resistance at 20°C under 500Vcc : |
≥ 20 000MΩ or 500MΩ.μF |
|
Dielectric withstanding voltage : |
>1.4 URC |
|
Temperature coefficient : |
-2200 ± 500 ppm/°C |
The dielectric constant of this ceramic, smaller than the dielectric constant of classical X7R materials, enables to manufacture about half the capacitance of X7R ranges when measured under standardized measurement conditions (Figure 4), what, at a first glance, appears, of course, to be a limitation.
Figure 4 : Comparison of capacitance ranges in the same size package for NPO, C48X and X7R
But this dielectric is very stable under voltage. The loss of capacitance versus dc voltage is only a couple of % (Figure 6) when it’s about 60% or more for classical X7R (2R1) ranges.
Figure 5 : capacitance change of C48 versus dc voltage
So, when looking at the capacitance value left under nominal voltage (working voltage), a simple calculation demonstrates it’s the same when using this ceramic and when using a X7R ceramic dielectric.
Furthermore the dissipation factor is very low, typically less than 0.05% what makes the heat dissipation in use not significant.
Under working conditions the capacitance values of this new range of products are equivalent to X7R values with the unrivaled advantage of no heat dissipation. Opposite to X7R, the C48X capacitors don’t suffer atemperature increase, what makes them more reliable.
… read more in the full paper link below.
CONCLUSION
The on-going evaluation and qualifications of ranges based on C48X material have been performed in order to answer to the increasing need of miniaturization of our customers.
The results obtained are fully compliant with our expectations and will enable to complete our existing space offer.
In addition, Exxelia pursues his efforts and continues to propose new ranges for next qualifications, with the help of CNES.
read the full technical paper in pdf here:
and presentation here: