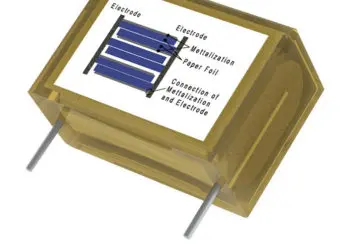
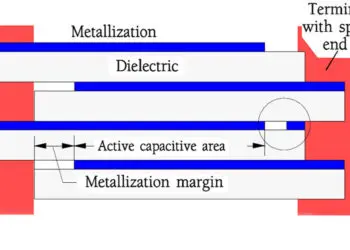
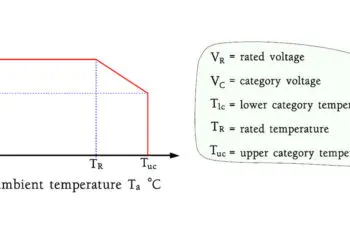
Other Inorganic Dielectrics
C 2.12 OTHER INORGANIC DIELECTRICS C 2.12.1 Class 3 ceramics The headlined type of ceramic capacitor are also called barrier layer capacitor. It consists of sintered granules of titanium oxides with semiconductor properties. On the surface of every granule there is created a capacitive barrier layer zone. The sum of ...